Laravel is an open-source PHP framework designed to make developing web apps mush easier and faster through built-in features. It is based on the MVC design pattern.
In this article, I will show you how to deploy a Laravel application to Azure App Services. The Azure web server is NGINX running on Linux version "Debian GNU/Linux 10 (buster)".
Assumptions
The following is assumed:
- You have Git, PHP and Composer installed on your computer.
- You have an Azure subscription
- You have a GitHub account
Getting Started
We will start our journey with a very simple Laravel application that lists some data from a SQLite database. Go into a working directory on your computer and run the following command from a terminal window to clone a GitHub repo:
git clone https://github.com/medhatelmasry/laravel-azure.git
It is a good idea to delete the .git folder on your computer.
Once the application is cloned, change directory to the cloned app and start your app as shown below:
cd laravel-azure
composer install
php artisan serve --port=8888
The web server will start on your computer listening on port 8888.
Starting Laravel development server: http://127.0.0.1:8888
[Sat Mar 26 15:36:29 2022] PHP 8.1.2 Development Server (http://127.0.0.1:8888) started
Point your browser to http://localhost:8888/ and you will see the following page:
For demo purposes, data is pulled from a SQLite database file at
database/autos.db.
Disclaimer: It is normal practice that the .env file is excluded from being pushed to source control. If you look at the .gitignore file, the line pertaining to .env is commented out because there is really no confidential information in this file.
Create a repository in your GitHub account and push the source code to it.
Create Azure App Service
Login to your Azure account by visiting
https://portal.azure.com. Enter "app services" in the filter field, then click on "App Services".
Click on "+ Create" on the top left-side.
On the "Create Web App Page", choose. your subscription then create new resource group.
Give your app a suitable host name that is unique.
Next, ensure these settings for
Publish,
Runtime stack and
Operating System:
Choose suitable values for the remaining settings based on your individual preference then click on the blue "Review + create" button:
Click on
Create button after you have reviewed your. choices.
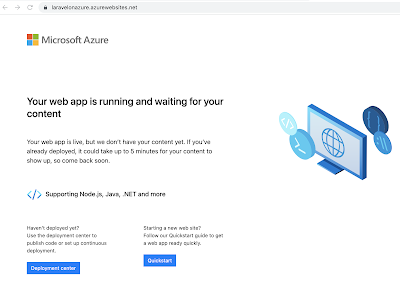
Once your app service is successfully provisioned, you can click on the "Go to resource" button.
You can see a default web page to your web app be clicking on the URL link on the top right-side.
The default page looks like this.
\
CI/CD pipeline
Of course, we want to deploy our Laravel PHP site from our GitHub repo. An easy way to achieve this is to use Azure's "Deployment Center". Click on "Deployment Center" in the left-side navigation.
In the "Deployment Center" blade, select
GitHub.
If this is your first time to connect Azure to your GitHub account, you will be asked to go through the GitHub authentication process. Thereafter, select the appropriate GitHub
Organization,
Repository and
Branch. My experience was:
Once you click on
Save, the deployment process commences.
To go to your GitHub repo, click on the
main link under
Branch.
To see the deployment in action, click on Actions in your GitHub repository.
Click on the workflow in progress.
The workflow will be going through a
build and
deploy process.
Be patient as it takes about 15 minutes to complete. This is because during
build the command "composer install" is executed. This produces a multitude of files under the vendors folder, which are thereafter sent to Azure. Once the workflow is completed, your GitHub workflow page will look like this:
The workflow files were automatically generated and placed a
.yml file in the
.github/workflows folder with your source code.
You can click on the .yml file to see what the file looks like.
At this point, it is worth going back to the code on your computer and doing a pull of your code so that you get a copy of the
.yml file that was added to your source code.
Configuring app on Azure
Back on the Azure portal, if you refresh the default page of our web app, you will experience a "403 Forbidden" message, which typically means that the root directory has no welcome page.
This is understandable because the main index.php page in Laravel resides in the /public folder. THis means that we need to do some configuration work on Azure.
In Azure, enter the term advanced in the search input field then click on "Advanced Tools".
A page opens up in a new browser tab. Click on SSH on the top menu.
A Linux terminal window is open.
If you are interested to know what version of Linux this is, enter the following terminal command:
cat /etc/os-release
The value beside PRETTY_NAME is the Linux distribution and version.
PRETTY_NAME="Debian GNU/Linux 10 (buster)"
NAME="Debian GNU/Linux"
VERSION_ID="10"
VERSION="10 (buster)"
VERSION_CODENAME=buster
ID=debian
HOME_URL="https://www.debian.org/"
SUPPORT_URL="https://www.debian.org/support"
BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugs.debian.org/"
We will make a copy of the existing nginx configuration and place the file inside the /home/site directory with the following command:
cp /etc/nginx/sites-available/default /home/site/default
Once copied, edit the /home/site/default file with nano or vi. I will use nano.
nano /home/site/default
Make the following changes:
| From | To | Around Line # |
| root /home/site/wwwroot | root /home/site/wwwroot/public | 6 |
location / {
index index.php index.html index.htm hostingstart.html;
}
|
location / {
index index.php index.html index.htm hostingstart.html;
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$query_string;
}
|
10 |
In nano, hit
CTRL X to save, enter
Y then hit
return.
We need to create a bash script file that overrides the existing default file with our customized version, then restart the server. Change directory to the site folder.
cd site
Inside the site directory, using vi or nano, create a file named startup.sh. To create a file with nano, type "nano startup.sh". Otherwise, to create a file with vi, type "vi startup.sh". Add the following content to startup.sh:
cp /home/site/default /etc/nginx/sites-available/default
We will make our bash script file executable with:
chmod u+x startup.sh
While in the terminal window on Azure, let's visit the folder that contains our Laravel application. Do this by going to the wwwroot folder.
cd wwwroot
ls -a
This reveals the existence of all the files that we had on GitHub plus files in the vendor folder.
Navigate back to your App Service via the Azure Portal. Select Configuration in the Settings section.
Click on the "General Settings" tab, enter "/home/site/startup.sh" for the "Startup Command", then click on
Save.
Click on blue
Continue button the the "Save changes" prompt.
Now, when you refresh the website, you should see that our web app is working as expected.
We have successfully deployed a database driven Laravel PHP application to Azure App Services through GitHub. I hope you use the principles you learned in this tutorial to deploy much more interesting Laravel applications.