Windows 8 has been available on MSDN for almost a month now. In addition, Windows 8 is now available to students under the Dreamspark program. At the moment, there are many among us who are using Windows 7 as our main operating system on our laptops and desktops. Some of us are willing to explore Windows 8 without necessarily losing our Windows 7 environment. A good way to accomplish this is to install Windows 8 as a VHD instance.
The assumption here is that you are installing Windows 8 on a computer that already has Windows 7.
Here are some advantages to using a VHD file to dual boot from:
- You can easily backup the VHD drive, thus backing up your entire Windows 8 operating system. It is particularly useful to do a backup of the VHD file right before installing a major piece of software that could potentially mess up your environment.
- You can move your VHD file from one computer to another.
- It acts exactly as if the Windows 8 operating is installed directly on a separate partition on your hard drive.
- You need not go through the pain of creating any additional partition on your hard drive.
Below are the steps you need to follow in order to accomplish this.
Steps for Installing Windows 8 in a VHD drive
- Create a DVD (or bootable USB) from the ISO image that you obtained with Windows 8 on it.
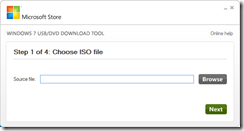
- To create a bootable USB from your ISO image, download a free utility from Microsoft at http://tinyurl.com/4qfdm4x. Here’s what the download looks like:
- To create a bootable DVD from your ISO image, place a blank DVD in the drive and simply double click on the ISO file. Windows 7 has a built-in application named “Windows Disk Image Burner”.
| Alternatively, you can use any other application that is capable of burning a DVD from an ISO file. I recommend a freely available application named “imgburn” that I use and like. |
- Reboot your computer from the DVD (or USB). This may require you to get into the BIOS settings of your computer in order to rearrange the boot sequence of your various storage devices.
- At the “Install Windows 8” screen, hit the Shift-F10 keys to open a command prompt.
- When at the command prompt, type "diskpart <enter>". Wait until you see the command prompt “DISKPART >”.
- In order to see a list of all available volumes, type "list volume <enter>". Identify the drive name that has ample available disk space which you want to install the VHD into. The drive letter will be under the column entitled “Ltr”.
- In this example, we will create the VHD file on drive D:. Make sure to replace D: with the appropriate drive letter that fits your situation. You can create either a fixed or dynamic VHD file:
- Creating a fixed VHD file: A fixed VHD file will allocate the entire maximum size that you set, regardless of whether or not the operating system uses that much space. Note that once you set a size, you cannot increase it in future, so make sure you are reasonably generous in choosing a maximum size. The following command assumes that you will be allocating a fixed VHD drive of 40GB (1GB = 1024 MB):
- Creating a dynamic expandable VHD file: A dynamic VHD file will initially be as large as the data used by the VHD. This can grow to the maximum size set when you create the VHD file. In the example below I will create a dynamic VHD drive that can grow to a maximum size of 40GB:
- Wait until the VHD drive has been 100% created. Next we need to select the VHD that was created. This is done by entering a command similar to the one below, depending on the drive letter and VHD file name you used:
- The next step is to attach to the VHD file. This is done with the the command:
- At this point we have done all that is necessary to create a VHD file and attach to it. We can now exit the DISKPART prompt. To do so, enter the following command:
| create vdisk file=D:\win8.vhd maximum=40960 Note: In the command above, substitute D: with the drive letter that suits your situation. You can use any other name you like instead of win8. |
| create vdisk file=D:\win8.vhd maximum=40960 type=expandable |
| select vdisk file=D:\win8.vhd |
| attach vdisk |
| exit |
- Close the command prompt window by clicking on the X located on the top-right-hand side of the window. We can now continue with the regular Windows 8 install.
- Click “Next” on the “Windows Setup” dialog.
- Click on the “Install Now” button on the next dialog.
- The next dialog will ask you for your product key. Enter your product key and click “Next”.
- Accept the license terms on the next dialog by clicking on the “I accept the license terms” checkbox then click on the “Next” button.
- The next dialog will enable you to choose whether you want to do an upgrade or custom install. Since we want to install Windows 8 from scratch, we will choose the second option “Custom: Install Windows only (advanced)” by clicking on it.
- The next window is very critical because it is at this point that you select the drive that will hold the new operating system. The primary manner by which you can identify this drive is by the size of the drive (I.E. in the case of this example it is 40GB) and the fact that it is still “Unallocated Space”.
- Note that you run the risk of losing data if you choose the wrong drive.
- Ignore the message “Windows can’t be installed on this drive. (Show details)
- The rest is should proceed smoothly. When the installation is finished, Windows 8 will be set as the default operating system. You will, however, be given the option to boot into Windows 7 if you so desire.
| Select the correct drive then click “Next”. |
Steps for removing the Windows 8 VHD
- Boot into Windows 7
- Find the Windows 8 VHD file on your hard drive
- Delete the Windows 8 VHD file
- Reboot the computer
Hope this is useful to you.
References:


No comments:
Post a Comment