In this walkthrough, we will build an MCP Server based on Azure Funtions and C#. It will be tested locally, then deployed to Azure using the az tool. To avoid confusion, we will go through this journey step-by-step. Although the methods we implement are very basic, the same concepts can be extended to cover much more sophisticated solutions.
MCP, what is that?
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is a specification created by Anthropic that makes it easier for AI applications to talk to tooling.
Why Remote MCP Servers?
Installing the same MCP server locally everywhere you need it is unrealistic. Making sure people on your team have the same version installed is a daunting task.
The solution is MCP servers that run remotely. As long as the endpoint supports server-side events (SSE), you are good to go.
Prerequisites
- .NET 9.0
- Visual Studio Code with Azure Tools extension
- Azure Functions Core Tools
- Azure CLI tool
- You need an Azure subscription to deploy the Functions app to Azure
Getting Started
We will create a vanilla C# console application with:
mkdir RemoteMcpFunc
cd RemoteMcpFunc
Open the console application in VS Code with:
code .
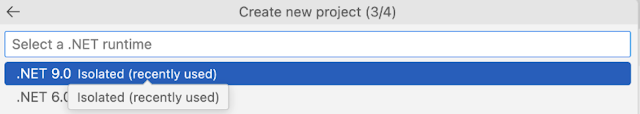
Click on the Azure tool on the left-side, then click on the "Azure Functions" tool and choose "Create New Project...".
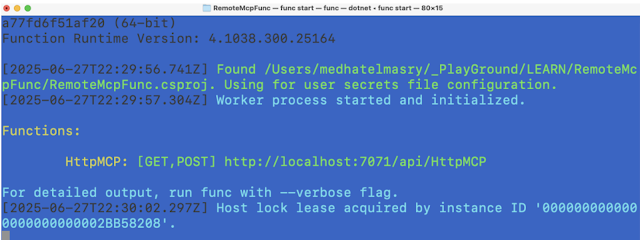
On the "Create new project" panel, choose the already highlighted current directory:Next, choose C#.Choose the latest version of .NET, which at the time of writing is ".NET 9.0 Isolated".We will keep it simple by choosing the "HTTP trigger" template.It the "Create new HTTP trigger" panel, provide a name for the Azure Function class file. In my case I simply named it HttpMCP.Next you will provide a namespace (like Mcp.Function).Again, to keep it simple, we will choose Anonymous.To make sure that our basic Azure Function works as expected, type this command in the root of your project:func start
This should show you output similar to this:
If you point your browser to the given URL, you will experience a welcome message similar to this:
Hit CTRL C to stop the application.
Add MCP package
At this stage our Azure Functions application has no MCP capability. We will change this by adding the following package:
dotnet add package Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker.Extensions.Mcp --prerelease
dotnet add package Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker.Extensions.Mcp --prerelease
NOTE: At this time, the above package is experimental and in pre-release mode.
Add MCP smarts
We will add three simple MCP server functions with these abilities:
- the classic Hello World
- reverse a message
- multiply two numbers
Add the following ToolDefinitions.cs class file:
public static class ToolDefinitions {
public static class HelloWorldTool {
public const string Name = "HelloWorldTool";
public const string Description = "A simple tool that says: Hello World!";
}
public static class ReverseMessageTool {
public const string Name = "ReverseMessageTool";
public const string Description = "Echoes back message in reverse.";
public static class Param {
public const string Name = "Message";
public const string Description = "The Message to reverse";
}
}
public static class MultiplyNumbersTool {
public const string Name = "MultiplyNumbersTool";
public const string Description = "A tool that shows paramater usage by asking for two numbers and multiplying them together";
public static class Param1 {
public const string Name = "FirstNumber";
public const string Description = "The first number to multiply";
}
public static class Param2 {
public const string Name = "SecondNumber";
public const string Description = "The second number to multiply";
}
}
public static class DataTypes {
public const string Number = "number";
public const string String = "string";
}
}
The above file contains tool names, descriptions and data types. There are three MCP tools that we will be creating:
| Name | Purpose | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| HelloWorldTool | Simply displays 'Hello World' | |
| ReverseMessageTool | Reverses text | string |
| MultiplyNumbersTool | Multiplies two numbers | number,number |
To keep things clean, we will create a separate class for each tool.
HelloWorldMcpTool.cs
public class HelloWorldMcpTool {
[Function("HelloWorldMcpTool")]
public IActionResult Run(
[McpToolTrigger(ToolDefinitions.HelloWorldTool.Name, ToolDefinitions.HelloWorldTool.Description)]
ToolInvocationContext context
) {
return new OkObjectResult($"Hi. I am {ToolDefinitions.HelloWorldTool.Name} and my message is 'HELLO WORLD!'");
}
}
ReverseMessageMcpTool.cs
public class ReverseMessageMcpTool {
[Function("ReverseMessageMcpTool")]
public IActionResult Run(
[McpToolTrigger(ToolDefinitions.ReverseMessageTool.Name, ToolDefinitions.ReverseMessageTool.Description)]
ToolInvocationContext context,
[McpToolProperty(ToolDefinitions.ReverseMessageTool.Param.Name, ToolDefinitions.DataTypes.String, ToolDefinitions.ReverseMessageTool.Param.Description)]
string message
) {
string reversedMessage = new string(message.ToCharArray().Reverse().ToArray());
return new OkObjectResult($"Hi. I'm {ToolDefinitions.ReverseMessageTool.Name}!. The reversed message is: {reversedMessage}");
}
}
MultiplyNumbersMcpTool.cs
public class MultiplyNumbersMcpTool {
[Function("MultiplyNumbersMcpTool")]
public IActionResult Run(
[McpToolTrigger(ToolDefinitions.MultiplyNumbersTool.Name, ToolDefinitions.MultiplyNumbersTool.Description)]
ToolInvocationContext context,
[McpToolProperty(ToolDefinitions.MultiplyNumbersTool.Param1.Name, ToolDefinitions.DataTypes.Number, ToolDefinitions.MultiplyNumbersTool.Param1.Description)]
int firstNumber,
[McpToolProperty(ToolDefinitions.MultiplyNumbersTool.Param2.Name, ToolDefinitions.DataTypes.Number, ToolDefinitions.MultiplyNumbersTool.Param2.Description)]
int secondNumber) {
return new OkObjectResult($"Hi. I am {ToolDefinitions.MultiplyNumbersTool.Name}!. The result of {firstNumber} multiplied by {secondNumber} is: {firstNumber * secondNumber}");
}
}
At this stage, we have created all the business logic for our three tools. What remains is configuring these tools in our Program.cs file. Add this code to Program.cs before: builder.Build().Run();
builder.EnableMcpToolMetadata();
builder.ConfigureMcpTool(ToolDefinitions.HelloWorldTool.Name);
builder.ConfigureMcpTool(ToolDefinitions.ReverseMessageTool.Name)
.WithProperty(ToolDefinitions.ReverseMessageTool.Param.Name, ToolDefinitions.DataTypes.String, ToolDefinitions.ReverseMessageTool.Param.Description);
builder.ConfigureMcpTool(ToolDefinitions.MultiplyNumbersTool.Name)
.WithProperty(ToolDefinitions.MultiplyNumbersTool.Param1.Name, ToolDefinitions.DataTypes.Number, ToolDefinitions.MultiplyNumbersTool.Param1.Description)
.WithProperty(ToolDefinitions.MultiplyNumbersTool.Param2.Name, ToolDefinitions.DataTypes.Number, ToolDefinitions.MultiplyNumbersTool.Param2.Description);
In local.settings.json, make the following changes:
- Set the value of AzureWebJobsStorage to "UseDevelopmentStorage=true" for local development with the Azure emulator.
- Inside the "Values" section, add: "AzureWebJobsSecretStorageType": "Files". This is to use local file system for secrets instead of blob storage.
Contents of local.settings.json will look like this:
{
"IsEncrypted": false,
"Values": {
"AzureWebJobsStorage": "UseDevelopmentStorage=true",
"FUNCTIONS_WORKER_RUNTIME": "dotnet-isolated",
"AzureWebJobsSecretStorageType": "Files"
}
}
Testing our MCP server locally
Start your Azure Functions app with:
func start
Note the MCP server SSE endpoint which will be later used to configure the server in VS Code.
Open the VS Code Command Palatte.Choose 'MCP: Add Server...".Next, choose "HTTP (HTTP or Server-Sent Events)".Paste the MCP server SSE endpoint. In my case it is http://localhost:7071/runtime/webhooks/mcp/sse.
Next, you will be asked to give your MCP Server a name. You can accept the defaut value.Select "Workspace Settings" so that the configuration is saved in your project in the .vscode/mcp.json file.The .vscode/mcp.json file is open in the editor.
{
"servers": {
"my-mcp-server-c5a639d4": {
"url": "http://localhost:7071/runtime/webhooks/mcp/sse"
}
}
}
Click on Start to start the MCP server.
Open the Open the GitHub Copilot Chat panel in the top right of VS Code.
In the chat panel, choose Agent, any Claude model, then click on the tools icon.Our three tools appear. This means that we can now use them.Back in the chat window, try this prompt:
Call the HelloWorldTool.
The MCP HelloWorldTool is detected. Click on the Continue button.
This is the respose I received:I also tried this prompt to test the reverse merssage tool.
Reverse the message: MCP is very cool
And, received this response:
Again, I tried this prompt to test the multiplication tool tool.
Multiply 100 and 89.
And, received this result:
Our Azure Functions MCP Server works well locally. The next challenge is to make it work remotely by deploying it to Azure.Deploy to Azure
We will use the az Azure CLI Tool. Folow these steps.
# Login to Azure
az login
# Create a resource group named: rg-mcp-func-server
az group create --name rg-mcp-func-server --location eastus
# Create a storage account named mcpstoreacc in resource-group rg-mcp-func-server in the eastus data center
az storage account create --name mcpstoreacc --resource-group rg-mcp-func-server --location eastus --sku Standard_LRS
# Create a function app named mcp-func-app
az functionapp create --resource-group rg-mcp-func-server --consumption-plan-location eastus --runtime dotnet-isolated --functions-version 4 --name mcp-func-app --storage-account mcpstoreacc
# Deploy (or redeploy) function app named mcp-func-app
func azure functionapp publish mcp-func-app
Upon successful deployment, the endpoint will be displayed in your terminal window:
Login into your Azure account and search for the resource group to find the deployed Azure Function.
Click on the functions app. In the example above, the functions app is named mcp-func-app. Copy the Default Domain and add to it https://. In .vscode/mcp.json replace http://localhost:7071 with the 'Default Domain' from Azure. Leave /runtime/webhooks/mcp/sse in the URL. Your .vscode/mcp.json will be similar to this:
{
"servers": {
"my-mcp-server-c5a639d4": {
//"url": "http://localhost:7071/runtime/webhooks/mcp/sse"
"url": "https://mcp-func-app.azurewebsites.net/runtime/webhooks/mcp/sse"
}
}
}
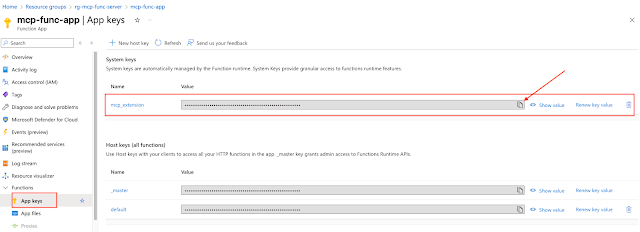
We will need to get an mcp_extension key from Azure. You will find that by clicking on "App keys" on the left navigarion in Azure and copying the mcp_extension key.
In .vscode/mcp.json, add this code above “servers”:
"inputs": [
{
"type": "promptString",
"id": "functions-mcp-extension-system-key",
"description": "Azure Functions MCP Extension System Key",
"password": true
}
],
.vscode/mcp.json looks like this:
The above added JSON will prompt the user to enter the mcp-extension key.
Again, in .vscode/mcp.json, add this “headers” block under “url”:
"headers": {
"x-functions-key": "${input:functions-mcp-extension-system-key}"
}
.vscode/mcp.json now looks like this:
When you start the server, you will be prompted for the MCP Extension System Key. Enter the mcp_extension key you obtained from Azure. Once the server is running again, you can start prompting it as before. The big difference this time is that it is running remotely, instead of on your local computer.
I entered this prompt:
Multiply 11 and 22 and provide the answer.
And received this result:
Conclusion
We have learned how to create MCP servers using Microsoft's Azure Functions technology with C#. We went through the development, testing, and deployment process. In general, this is a much more compelling solution for large scale implementations of MCP Servers. You can take these basic concepts and build bigger and better MCP Servers.